DiT: U-Net 버리고 Transformer 쓰니까 Scaling Law가 적용됐다 (Sora 기반기술)
U-Net은 크기 키워도 성능 향상이 수확체감. DiT는 모델이 클수록 일관되게 좋아집니다. Sora의 기반이 된 아키텍처 완전 분석.
DiT: Diffusion Transformer, U-Net을 넘어선 새로운 패러다임
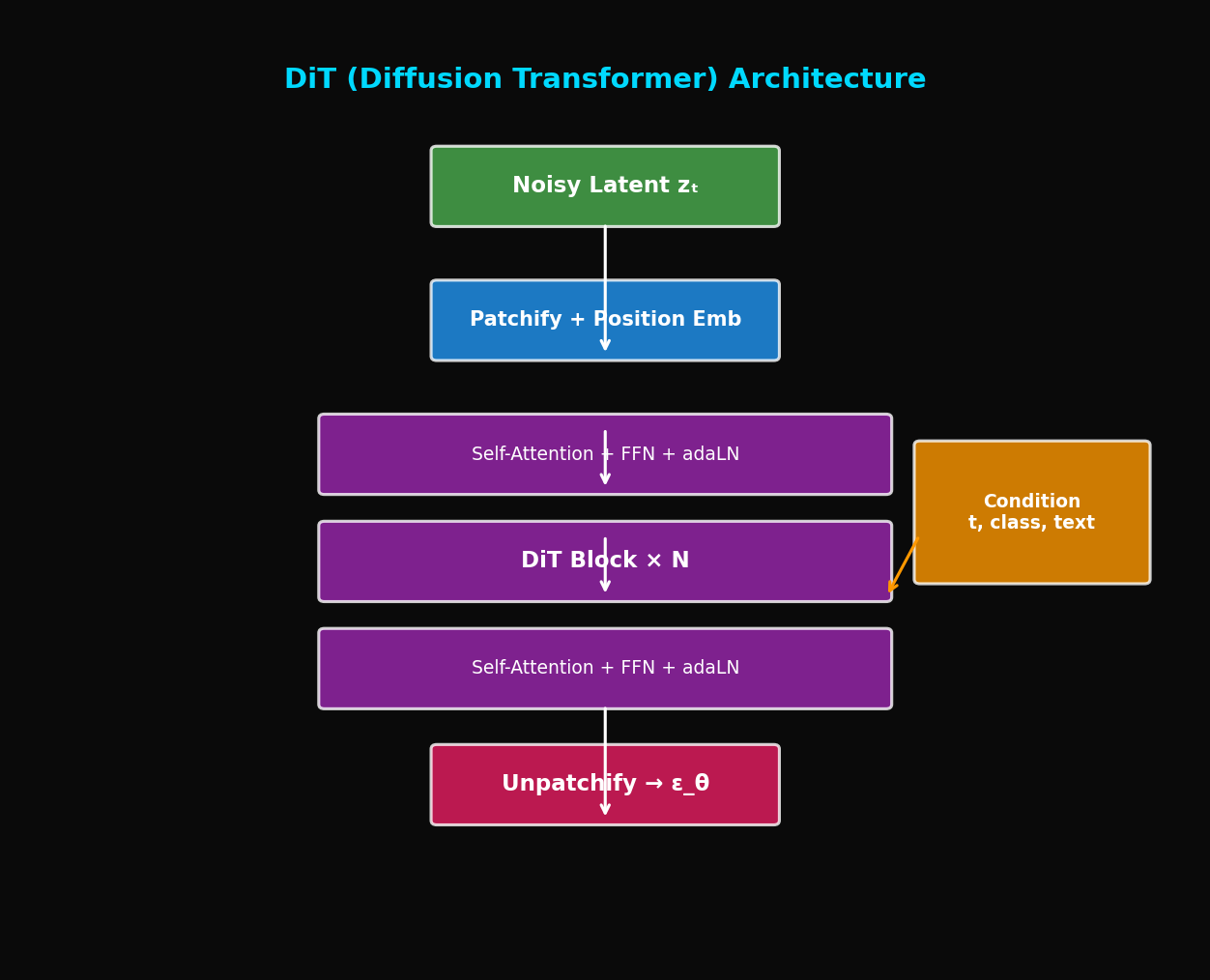
TL;DR: DiT는 Diffusion 모델의 backbone을 U-Net에서 Vision Transformer로 교체합니다. Scaling law가 적용되어 모델이 커질수록 성능이 일관되게 향상됩니다. Sora의 기반 기술입니다.
1. U-Net의 한계
1.1 왜 U-Net이었나?
DDPM부터 Stable Diffusion까지, 모든 주요 Diffusion 모델이 U-Net을 사용한 이유:
- Skip Connections: 고해상도 정보 보존
- Multi-scale Processing: 다양한 해상도의 특징 추출
- Proven Architecture: 세그멘테이션에서 검증됨
1.2 U-Net의 문제점
하지만 U-Net에는 근본적인 한계가 있습니다:
1. Scaling이 어려움
U-Net channels ↑ → 파라미터 ∝ channels²
연산량이 quadratically 증가
2. Inductive Bias
- CNN의 local connectivity 가정
- 전역적 정보 처리에 비효율적
- Attention 블록으로 보완하지만 완벽하지 않음
3. 비일관적 Scaling
| U-Net Size | Parameters | FID 개선 |
|---|---|---|
| Small | 100M | baseline |
| Medium | 400M | -15% |
| Large | 900M | -8% |
| XL | 2B | -3% |
수확 체감 현상 발생
1.3 Transformer의 가능성
반면 Vision Transformer는:
- 일관된 Scaling: 크기에 비례하여 성능 향상
- 전역 처리: Self-attention으로 모든 패치 간 관계 학습
- 검증된 Scaling Law: GPT, LLaMA에서 증명됨
2. DiT 아키텍처
2.1 핵심 아이디어
"Diffusion 모델에서 U-Net을 Vision Transformer로 대체하자"
2.2 입력 처리: Patchify
이미지(또는 latent)를 패치로 분할:
class PatchEmbed(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, img_size=32, patch_size=2, in_channels=4, embed_dim=768):
super().__init__()
self.num_patches = (img_size // patch_size) ** 2
self.proj = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, embed_dim, patch_size, stride=patch_size)
def forward(self, x):
# x: (B, C, H, W) → (B, num_patches, embed_dim)
x = self.proj(x) # (B, embed_dim, H', W')
x = x.flatten(2).transpose(1, 2) # (B, num_patches, embed_dim)
return x예시 (Stable Diffusion latent):
- 입력: 64×64×4 latent
- 패치 크기: 2×2
- 패치 수: 32×32 = 1024개
- 각 패치: 2×2×4 = 16 → embed_dim으로 projection
2.3 Condition 주입: AdaLN
기존 U-Net: Time embedding을 ResBlock에 더함
DiT: Adaptive Layer Normalization (AdaLN)
여기서 는 condition에서 생성된 scale/shift 파라미터
class AdaLN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_size, condition_dim):
super().__init__()
self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(hidden_size, elementwise_affine=False)
self.adaLN_modulation = nn.Sequential(
nn.SiLU(),
nn.Linear(condition_dim, 6 * hidden_size)
)
def forward(self, x, c):
# c: condition (time + class embedding)
shift_msa, scale_msa, gate_msa, shift_mlp, scale_mlp, gate_mlp = \
self.adaLN_modulation(c).chunk(6, dim=-1)
# 각 블록에서 사용
return shift_msa, scale_msa, gate_msa, shift_mlp, scale_mlp, gate_mlp2.4 DiT Block
class DiTBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_size, num_heads, condition_dim, mlp_ratio=4.0):
super().__init__()
self.norm1 = nn.LayerNorm(hidden_size, elementwise_affine=False)
self.attn = Attention(hidden_size, num_heads)
self.norm2 = nn.LayerNorm(hidden_size, elementwise_affine=False)
self.mlp = MLP(hidden_size, int(hidden_size * mlp_ratio))
# AdaLN modulation
self.adaLN_modulation = nn.Sequential(
nn.SiLU(),
nn.Linear(condition_dim, 6 * hidden_size)
)
def forward(self, x, c):
# c: condition embedding
shift_msa, scale_msa, gate_msa, shift_mlp, scale_mlp, gate_mlp = \
self.adaLN_modulation(c).chunk(6, dim=-1)
# Self-attention with AdaLN
x_norm = self.norm1(x)
x_norm = x_norm * (1 + scale_msa.unsqueeze(1)) + shift_msa.unsqueeze(1)
x = x + gate_msa.unsqueeze(1) * self.attn(x_norm)
# MLP with AdaLN
x_norm = self.norm2(x)
x_norm = x_norm * (1 + scale_mlp.unsqueeze(1)) + shift_mlp.unsqueeze(1)
x = x + gate_mlp.unsqueeze(1) * self.mlp(x_norm)
return x2.5 출력 처리: Unpatchify
패치들을 다시 이미지로 재구성:
class FinalLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_size, patch_size, out_channels):
super().__init__()
self.norm_final = nn.LayerNorm(hidden_size, elementwise_affine=False)
self.linear = nn.Linear(hidden_size, patch_size * patch_size * out_channels)
self.adaLN_modulation = nn.Sequential(
nn.SiLU(),
nn.Linear(hidden_size, 2 * hidden_size)
)
def forward(self, x, c):
shift, scale = self.adaLN_modulation(c).chunk(2, dim=-1)
x = self.norm_final(x) * (1 + scale.unsqueeze(1)) + shift.unsqueeze(1)
x = self.linear(x)
return x
def unpatchify(x, patch_size, img_size):
"""
x: (B, num_patches, patch_size²×C)
→ (B, C, H, W)
"""
p = patch_size
h = w = img_size // p
c = x.shape[-1] // (p * p)
x = x.reshape(x.shape[0], h, w, p, p, c)
x = torch.einsum('nhwpqc->nchpwq', x)
x = x.reshape(x.shape[0], c, h * p, w * p)
return x3. 전체 DiT 모델
3.1 모델 정의
class DiT(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
input_size=32, # Latent size
patch_size=2,
in_channels=4,
hidden_size=1152,
depth=28,
num_heads=16,
mlp_ratio=4.0,
num_classes=1000, # For class conditioning
learn_sigma=True,
):
super().__init__()
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.out_channels = in_channels * 2 if learn_sigma else in_channels
self.patch_size = patch_size
self.num_heads = num_heads
# Patch embedding
self.x_embedder = PatchEmbed(input_size, patch_size, in_channels, hidden_size)
num_patches = self.x_embedder.num_patches
# Time embedding
self.t_embedder = TimestepEmbedder(hidden_size)
# Class embedding
self.y_embedder = LabelEmbedder(num_classes, hidden_size)
# Positional embedding
self.pos_embed = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, num_patches, hidden_size))
# DiT blocks
self.blocks = nn.ModuleList([
DiTBlock(hidden_size, num_heads, hidden_size, mlp_ratio)
for _ in range(depth)
])
# Final layer
self.final_layer = FinalLayer(hidden_size, patch_size, self.out_channels)
self.initialize_weights()
def forward(self, x, t, y):
"""
x: (B, C, H, W) noisy latent
t: (B,) timesteps
y: (B,) class labels
"""
# Patchify + positional embedding
x = self.x_embedder(x) + self.pos_embed
# Condition embedding
t = self.t_embedder(t)
y = self.y_embedder(y)
c = t + y # Combined condition
# DiT blocks
for block in self.blocks:
x = block(x, c)
# Final layer
x = self.final_layer(x, c)
# Unpatchify
x = unpatchify(x, self.patch_size, self.input_size)
return x3.2 모델 Variants
| Model | Layers | Hidden Size | Heads | Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DiT-S | 12 | 384 | 6 | 33M |
| DiT-B | 12 | 768 | 12 | 130M |
| DiT-L | 24 | 1024 | 16 | 458M |
| DiT-XL | 28 | 1152 | 16 | 675M |
4. Scaling Law 분석
4.1 모델 크기 vs 성능
DiT 논문의 핵심 발견:
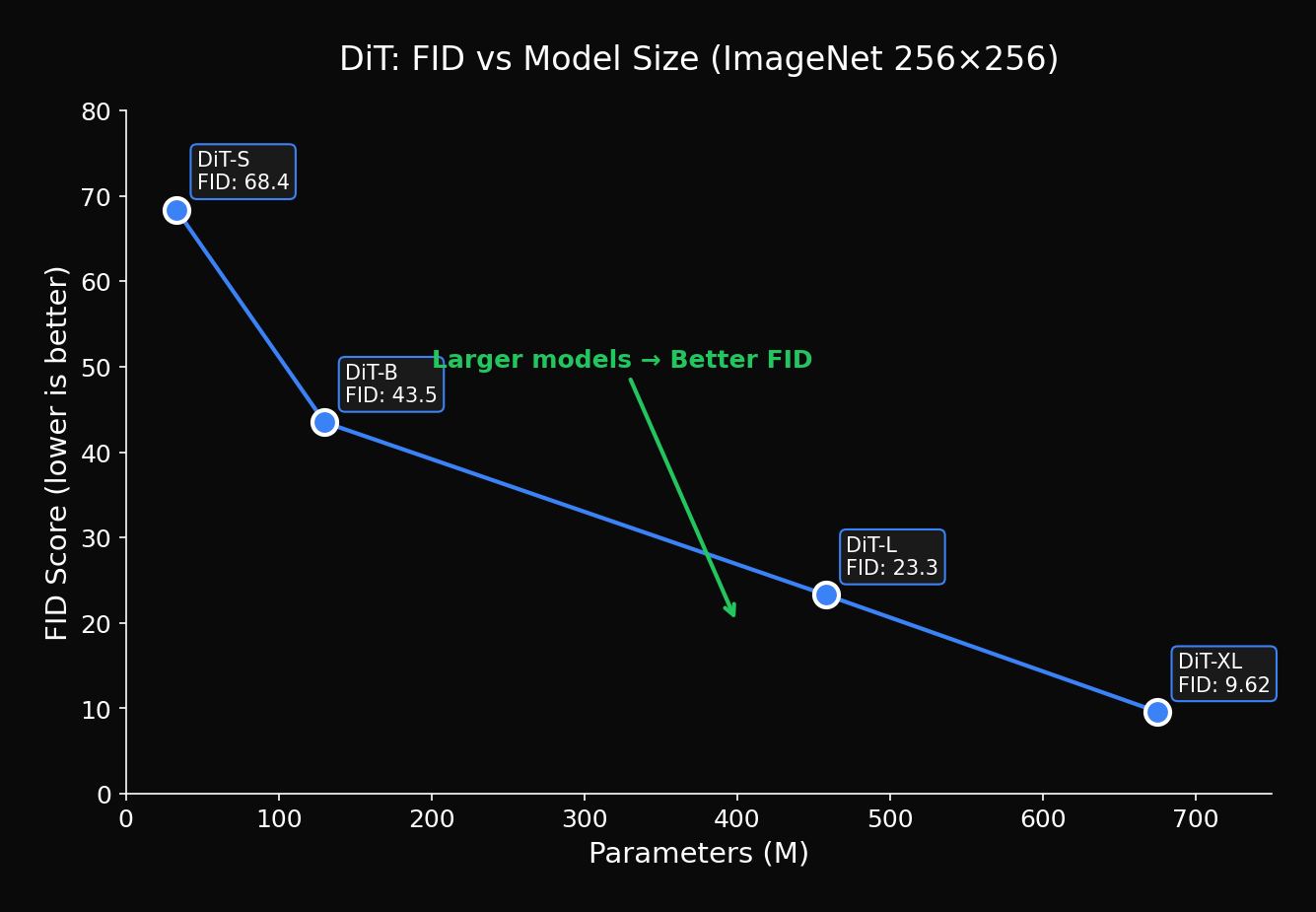
일관된 개선: 파라미터 증가에 따라 FID가 지속적으로 감소
4.2 Compute vs 성능
| Compute (GFLOPs) | DiT FID | U-Net FID |
|---|---|---|
| 50 | 43.5 | 52.3 |
| 100 | 25.1 | 31.8 |
| 200 | 12.4 | 18.6 |
| 500 | 4.9 | 9.3 |
같은 연산량에서 DiT가 더 효율적
4.3 Scaling Law Formula
경험적으로 발견된 관계:
여기서:
- : 연산량 (GFLOPs)
- for DiT
- for U-Net
DiT의 scaling exponent가 더 큼 → 스케일링에 더 유리
5. 학습 및 샘플링
5.1 학습 코드
def train_step(model, vae, x, y, noise_scheduler):
# 1. Encode to latent
with torch.no_grad():
z = vae.encode(x).latent_dist.sample() * 0.18215
# 2. Sample timestep
t = torch.randint(0, noise_scheduler.num_train_timesteps, (z.shape[0],))
# 3. Add noise
noise = torch.randn_like(z)
z_t = noise_scheduler.add_noise(z, noise, t)
# 4. Predict noise (or v-prediction)
model_output = model(z_t, t, y)
# 5. Compute loss
if model.learn_sigma:
noise_pred, _ = model_output.chunk(2, dim=1)
else:
noise_pred = model_output
loss = F.mse_loss(noise_pred, noise)
return loss5.2 Classifier-Free Guidance
@torch.no_grad()
def sample(model, vae, num_samples, num_classes, cfg_scale=4.0, num_steps=250):
# Random class labels
y = torch.randint(0, num_classes, (num_samples,))
y_null = torch.full_like(y, num_classes) # Null class
# Initial noise
z = torch.randn(num_samples, 4, 32, 32)
# Sampling loop
for t in tqdm(reversed(range(num_steps))):
t_batch = torch.full((num_samples,), t)
# CFG: predict both conditional and unconditional
z_input = torch.cat([z, z], dim=0)
t_input = torch.cat([t_batch, t_batch], dim=0)
y_input = torch.cat([y, y_null], dim=0)
model_output = model(z_input, t_input, y_input)
eps_cond, eps_uncond = model_output.chunk(2, dim=0)
# Guidance
eps = eps_uncond + cfg_scale * (eps_cond - eps_uncond)
# DDPM step
z = ddpm_step(z, eps, t)
# Decode
z = z / 0.18215
images = vae.decode(z).sample
return images6. DiT의 응용
6.1 Sora (OpenAI)
Sora는 DiT를 비디오 생성으로 확장:
Video DiT:
- 입력: 3D latent (T × H × W × C)
- Patchify: Spacetime patches
- Attention: Spatial + Temporal
- Output: Video frames
핵심 변경점:
- 2D patches → 3D patches
- 2D positional encoding → 3D positional encoding
- Cross-frame attention 추가
6.2 Flux (Black Forest Labs)
Flux는 DiT를 T2I에 최적화:
- MMDiT (Multimodal DiT): Text-image joint attention
- Rectified Flow: 더 빠른 샘플링
- 더 큰 스케일: 12B 파라미터
6.3 PixArt 시리즈
PixArt-α, PixArt-Σ:
- 효율적인 학습 (10% 비용)
- T5 text encoder 사용
- Class-to-text 전이 학습
7. 구현 최적화
7.1 Flash Attention
from flash_attn import flash_attn_func
class FlashAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, num_heads):
super().__init__()
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.head_dim = dim // num_heads
self.qkv = nn.Linear(dim, dim * 3)
self.proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
def forward(self, x):
B, N, C = x.shape
qkv = self.qkv(x).reshape(B, N, 3, self.num_heads, self.head_dim)
q, k, v = qkv.unbind(2)
# Flash Attention
out = flash_attn_func(q, k, v)
out = out.reshape(B, N, C)
return self.proj(out)7.2 Gradient Checkpointing
class DiTWithCheckpoint(DiT):
def forward(self, x, t, y):
x = self.x_embedder(x) + self.pos_embed
c = self.t_embedder(t) + self.y_embedder(y)
# Gradient checkpointing for memory efficiency
for block in self.blocks:
x = checkpoint(block, x, c, use_reentrant=False)
x = self.final_layer(x, c)
return unpatchify(x, self.patch_size, self.input_size)7.3 Mixed Precision Training
from torch.cuda.amp import autocast, GradScaler
scaler = GradScaler()
for batch in dataloader:
with autocast():
loss = train_step(model, vae, batch['image'], batch['label'])
scaler.scale(loss).backward()
scaler.step(optimizer)
scaler.update()8. 실험 결과
8.1 ImageNet 256×256
| Model | FID ↓ | IS ↑ | Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| ADM | 10.94 | 100.98 | 554M |
| LDM-4 | 10.56 | 103.49 | 400M |
| **DiT-XL/2** | **2.27** | **278.24** | 675M |
DiT-XL이 SOTA 달성!
8.2 ImageNet 512×512
| Model | FID ↓ | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| ADM-G | 7.72 | 608M |
| **DiT-XL/2** | **3.04** | 675M |
8.3 Scaling 실험
| Model | GFLOPs | FID |
|---|---|---|
| DiT-S/2 | 6 | 68.4 |
| DiT-B/2 | 23 | 43.5 |
| DiT-L/2 | 80 | 23.3 |
| DiT-XL/2 | 119 | 9.6 |
| DiT-XL/2 (더 긴 학습) | 119 | 2.27 |
9. 결론
DiT는 Diffusion 모델의 새로운 시대를 열었습니다:
- Scalable Architecture: Transformer의 scaling law 활용
- 일관된 성능 향상: 크기에 비례하는 품질
- 범용성: 이미지, 비디오, 3D 등 다양한 modality 지원
- 효율성: 같은 연산량에서 더 좋은 성능
Sora, Flux 등 최신 생성 모델들이 DiT 기반인 이유입니다.
다음 글에서는 PixArt-α를 다룹니다: DiT를 효율적으로 학습하는 방법과 T5 text encoder의 활용.
References
- Peebles, W., & Xie, S. (2023). Scalable Diffusion Models with Transformers. ICCV 2023
- Dosovitskiy, A., et al. (2021). An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale. ICLR 2021
- Chen, J., et al. (2023). PixArt-α: Fast Training of Diffusion Transformer for Photorealistic Text-to-Image Synthesis. arXiv
- Esser, P., et al. (2024). Scaling Rectified Flow Transformers for High-Resolution Image Synthesis. arXiv
Tags: #DiT #Diffusion-Transformer #Scaling-Law #Sora #Vision-Transformer #이미지생성
이 글의 전체 코드는 첨부된 Jupyter Notebook에서 확인할 수 있습니다.
이메일로 받아보기
관련 포스트

SDFT: 자기 증류로 망각 없이 학습하기
복잡한 강화학습 없이, 모델이 스스로를 선생님 삼아 새로운 기술을 배우면서도 기존 능력을 유지하는 방법.

Qwen3-Max-Thinking 스냅샷 공개: 추론형 AI의 새로운 기준
최근 LLM 시장의 트렌드는 단순히 '더 많은 데이터'를 학습하는 것을 넘어, 모델이 '어떻게 생각하느냐'에 집중하고 있습니다. 알리바바 클라우드(Alibaba Cloud)가 자사의 가장 강력한 모델 Qwen3-Max-Thinking의 API 스냅샷(qwen3-max-2026-01-23)을 공개했습니다.

YOLO26: Upgrade or Hype? 완벽 가이드
2026년 1월 출시된 YOLO26의 핵심 기능, YOLO11과의 성능 비교, 그리고 실제 업그레이드 가치가 있는지 실습과 함께 분석합니다.